Introduction to IoT Predictive Maintenance
In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, unplanned downtime isn’t just a minor inconvenience—it’s a major cost driver.
Predictive maintenance enhanced by the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how businesses maintain their equipment and optimize operations. This innovative approach combines data analytics with foresight, allowing you to foresee potential failures and take proactive measures to prevent them.
This blog provides a detailed overview of IoT predictive maintenance, covering its market growth, benefits, key components, and implementation steps. It contrasts predictive maintenance with preventative maintenance, highlights industry-specific applications, addresses challenges, and explores future trends in the field.
Predictive Maintenance Market Size
The predictive maintenance market is experiencing significant growth. It’s projected to expand from USD 10.6 billion in 2024 to USD 47.8 billion by 2029.
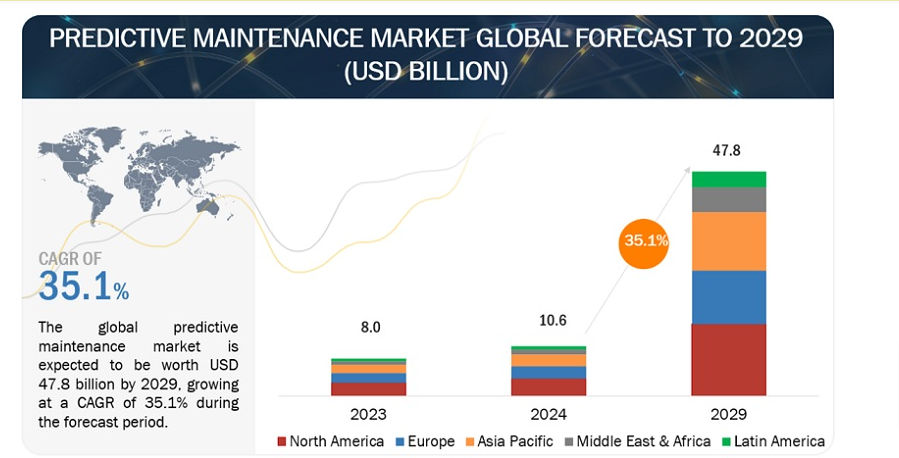
A report by Fact.MR further indicates that the market will increase from USD 9.1 billion in 2024 to USD 59 billion by 2034, with a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5%. This growth is driven by advancements in IoT, which allow businesses to manage equipment more effectively and allocate resources more efficiently.
Breakup by Technique:
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a proactive approach that leverages data and analytics to foresee equipment failures before they happen. Unlike traditional methods, which may rely on scheduled or reactive maintenance, predictive maintenance focuses on real-time monitoring of equipment conditions. It aims to identify potential issues before they result in unplanned downtime, thus enhancing operational efficiency.
What is IoT Predictive Maintenance?
IoT predictive maintenance involves using the Internet of Things to collect and analyze data about equipment and machinery. Sensors and monitors gather real-time data on equipment status and performance. This data is then processed by predictive maintenance software or other smart systems to identify potential issues that could lead to downtime.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate over the internet. These devices—such as sensors and monitors—continuously transmit valuable data about equipment conditions. By analyzing this data, organizations can anticipate and address potential equipment failures proactively.
Predictive Maintenance vs. Preventative Maintenance
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance | Preventative Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance performed based on real-time data and condition monitoring. | Maintenance performed at regular intervals based on predefined schedules. |
| Goal | To predict and prevent potential failures before they occur. | To prevent equipment failure by regularly scheduled maintenance. |
| Approach | Data-driven, uses sensors and analytics to monitor equipment condition. | Time-based, relies on manufacturer’s recommendations and historical data. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in technology and sensors, lower long-term costs. | Lower initial costs, potentially higher long-term costs due to unnecessary maintenance. |
| Efficiency | High, as it minimizes unplanned downtime and extends equipment life. | Moderate, as it may result in unnecessary maintenance and downtime. |
| Implementation | Requires advanced technology, skilled personnel, and continuous monitoring. | Easier to implement, does not require advanced technology or continuous monitoring. |
| Data Requirement | Requires continuous data collection and analysis. | Requires historical data for scheduling maintenance. |
| Examples of Use | Complex and critical systems like industrial machinery, aviation, and utilities. | General manufacturing equipment, vehicles, HVAC systems. |
| Advantages | Reduces unexpected failures, optimizes maintenance schedules, extends equipment life. | Simple to understand and implement, consistent maintenance routine. |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial cost, requires advanced technology and expertise. | Can lead to over-maintenance, not as effective in preventing unexpected failures. |
| Downtime | Minimizes downtime through timely maintenance. | Scheduled downtime, which may not always align with equipment condition. |
| Examples | Using IoT sensors to monitor equipment vibrations and predict failures. | Changing oil in machinery every six months regardless of condition. |
Predictive maintenance and preventative maintenance are distinct approaches to managing equipment reliability:
- Preventative Maintenance: This method follows a time-based or schedule-driven approach. Equipment is serviced at regular intervals, regardless of its current condition. While this can prevent some issues, it often results in unnecessary maintenance, increased costs, and wasted resources. Preventative maintenance assumes that equipment failures are primarily age-related, which is only accurate 18% of the time.
- Predictive Maintenance: This approach provides a more objective view of equipment health. By analyzing real-time and historical data, predictive maintenance determines the optimal time for repairs, minimizing production impact and optimizing spare part usage. It enables maintenance teams to focus on repairs as needed, enhancing equipment uptime and operational efficiency.
Predictive maintenance empowers maintenance teams to:
- Prioritize repairs based on actual equipment condition.
- Optimize spare part inventory and reduce unnecessary procurement.
- Maximize team efficiency and minimize downtime.
By adopting predictive maintenance, organizations can transition from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, leading to improved operational performance and cost savings.
Key Components:
- IoT Sensors: Collect real-time data on equipment performance
- Data Analytics: Process and analyze sensor data to identify patterns
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Predict potential failures based on historical and real-time data
- Cloud Computing: Store and process large amounts of data
- User Interface: Present insights and alerts to maintenance teams
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance with IoT
Implementing predictive maintenance with IoT offers several significant benefits:
- Reduced Downtime: By predicting equipment failures before they occur, predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Cost Savings: IoT-driven predictive maintenance reduces maintenance costs by addressing issues before they escalate and avoiding unnecessary maintenance activities.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Regular and timely maintenance based on actual equipment conditions extends the lifespan of machinery and reduces the frequency of replacements.
- Enhanced Safety: Predictive maintenance helps identify potential safety hazards early, improving overall workplace safety and reducing the risk of accidents.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: By optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing equipment failures, businesses can achieve higher operational efficiency and reliability.
“According to McKinsey & Company research, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30%, reduce downtime by up to 45%, and extend equipment life by up to 20%.”
IoT Predictive Maintenance: Implementation Steps & Best Practices
To successfully implement predictive maintenance with IoT, consider the following steps:
- Identify Key Equipment: Determine which equipment will benefit most from predictive maintenance. Focus on critical assets that have a significant impact on operations.
- Deploy IoT Sensors: Install IoT sensors on the identified equipment to start collecting real-time data. Ensure that sensors are chosen based on the specific parameters you need to monitor.
- Choose Analytics Tools: Utilize analytics tools and machine learning algorithms to process and analyze the data collected by IoT sensors. These tools will help identify patterns and predict potential failures.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Ensure that the predictive maintenance system integrates seamlessly with your existing operational technology (OT) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- Train Your Team: Provide training for your maintenance team to effectively use the predictive maintenance tools and interpret the insights provided by IoT data.
- Continuously Monitor and Improve: Regularly review and refine your predictive maintenance processes based on the data and feedback. Continuously monitor the performance of your system to ensure its effectiveness.
IoT Predictive Maintenance Across Industries
IoT-based predictive maintenance is enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime across various industries. Here’s how it’s applied in different sectors:
1. IoT-Powered Predictive Maintenance in Transportation and Logistics
- Early Detection of Issues: Sensors monitor fleet vehicle health, identifying potential problems before they cause failures.
- Optimized Maintenance Scheduling: Automate and plan maintenance tasks to prevent breakdowns and ensure reliable fleet operation.
2. IoT Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing Equipment
- Temperature Monitoring: Infrared sensors track equipment temperature, preventing overheating and potential failures.
- Data-Driven Maintenance Plans: Analyze real-time data to create effective maintenance schedules, reducing unplanned downtime.
3. IoT-Based Predictive Maintenance in Energy Infrastructure and Utilities
- Outage Prevention: Predictive maintenance tools analyze sensor data to identify factors leading to potential outages.
- AI-Enhanced Maintenance: Artificial intelligence develops proactive maintenance plans to prevent service interruptions.
4. IoT-Enabled Predictive Maintenance in Healthcare
- Equipment Monitoring: Sensors monitor storage conditions for pharmaceutical products, ensuring compliance and integrity.
- Timely Maintenance: Detect and address equipment malfunctions to avoid impacting patient care.
5. IoT Predictive Maintenance in Smart Homes, Buildings, and Cities
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT sensors track systems like HVAC and lighting, optimizing performance and efficiency.
- Enhanced Automation: Automate maintenance tasks and respond quickly to issues, improving building management and energy use.
Challenges and Considerations:
Implementing IoT-based predictive maintenance can significantly enhance operational efficiency, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these challenges effectively is crucial for a successful transition and realization of the benefits. Here’s an in-depth look at the key challenges and considerations:
1. Data Security: Protect Sensitive Operational Data
Data security is a major concern when integrating IoT technologies into predictive maintenance systems. As equipment and systems become more interconnected, the volume of data collected increases, including sensitive operational information. Ensuring this data is protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats is critical. To address data security concerns:
- Implement Robust Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Adopt Comprehensive Cybersecurity Measures: Use firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits to safeguard against threats.
- Follow Compliance Standards: Adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, to ensure data protection.
2. Integration: Seamlessly Incorporate New Tech with Legacy Systems
Integration of new IoT technologies with existing legacy systems can be complex. Many organizations rely on older systems that may not be directly compatible with modern IoT solutions. To facilitate smooth integration:
- Evaluate Compatibility: Assess the compatibility of your current systems with new IoT solutions before implementation.
- Use Middleware: Employ middleware solutions that can bridge the gap between old and new systems, ensuring seamless data flow.
- Plan for Gradual Upgrades: Implement IoT solutions in phases, starting with non-critical systems to minimize disruption and ensure compatibility
3. ROI Justification: Demonstrate Value to Secure Buy-In from Stakeholders
ROI justification is essential for securing approval and funding for predictive maintenance projects. Demonstrating the value and potential return on investment can be challenging. To effectively justify ROI:
- Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis: Compare the costs of implementing IoT-based predictive maintenance with the anticipated savings from reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and increased efficiency.
- Present Real-World Case Studies: Share successful case studies and industry examples that highlight tangible benefits and improvements.
- Develop a Clear Business Case: Outline the strategic advantages, operational benefits, and financial gains in a detailed business case to present to stakeholders.
4. Skill Gap: Train or Hire Staff with Necessary Data Analysis Skills
The skill gap is a significant challenge in deploying IoT-based predictive maintenance. Adequate data analysis skills are essential to interpret the data generated by IoT devices and derive actionable insights. To address this gap:
- Invest in Training Programs: Provide training programs to upskill existing employees in data analysis and IoT technologies.
- Hire Skilled Professionals: Recruit professionals with expertise in data analysis, IoT, and predictive maintenance to strengthen your team.
- Foster a Data-Driven Culture: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and data-driven decision-making within your organization
Future Trends:
- AI and Machine Learning Advancements: More accurate predictions
- Edge Computing: Faster processing of IoT data
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas for enhanced monitoring and simulation
- 5G Integration: Improved connectivity for IoT devices
How Rejig Digital Can Help You Get Started with IoT-enabled Predictive Maintenance?
At Rejig Digital, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge IoT-enabled predictive maintenance solutions designed to enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Here’s how our products can transform your predictive maintenance strategy:
- Ally: AI-driven tool for predicting failures and reducing downtime.
- Accrue: Provides financial insights and optimizes maintenance costs.
- Arete: IoT platform for unified operational visibility.
- Connected Asset & Connected Workmen: Integrates machinery and workforce for peak performance.
Transform your operations with our tailored solutions. Contact us today for a consultation and start optimizing your maintenance strategy.
Conclusion:
Predictive maintenance with IoT is not just a trend—it’s the future of industrial maintenance. By embracing this technology, businesses can significantly reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
FAQ
- What is the application of IoT in maintenance?
IoT applications in maintenance involve using interconnected sensors and devices to monitor equipment conditions in real time. These sensors collect data on various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and pressure, which helps detect anomalies and predict potential equipment failures before they occur.
- What is predictive analysis in IoT?
Predictive analysis in IoT refers to using advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze data collected from IoT sensors. This analysis helps identify patterns and trends that indicate potential equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance actions to prevent unplanned downtime.
- What is an example of IoT maintenance?
An example of IoT maintenance is using sensors on a factory’s HVAC system to monitor its performance. The sensors collect data on temperature and airflow, which is analyzed to predict when components might fail. Maintenance is then scheduled based on this analysis, rather than on a fixed timetable or after a breakdown occurs.
- What is preventive maintenance of IoT sensors?
Preventive maintenance of IoT sensors involves regular checks and servicing to ensure that the sensors themselves are functioning correctly. This includes calibrating the sensors, cleaning them, and replacing any components that may be worn out. This helps in maintaining accurate data collection and ensuring reliable performance.
- What is predictive maintenance in IoT?
Predictive maintenance in IoT uses data collected from IoT sensors to predict when equipment is likely to fail. By analyzing this data with advanced algorithms, organizations can perform maintenance activities just in time to prevent failures, thereby reducing unplanned downtime and extending the life of their assets.
- What is the role of IoT and big data analytics in predictive maintenance?
IoT provides the data through interconnected sensors, while big data analytics processes this data to extract meaningful insights. Together, they enable predictive maintenance by identifying patterns and anomalies that signal potential issues, allowing for timely and targeted maintenance actions.
- What is the size of the predictive maintenance market in IoT?
The predictive maintenance market within IoT is rapidly growing. As of recent estimates, it is expected to reach several billion dollars by the mid-2020s. This growth is driven by increasing adoption of IoT technologies in various industries to enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
- How is IIoT used for predictive maintenance of machines in the industry?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) uses sensors and connected devices to monitor machine performance in real-time. IIoT systems collect data on machine conditions, which is analyzed to predict potential failures. This allows for scheduled maintenance based on the actual condition of the machines, improving reliability and reducing downtime.
- What is big data for predictive maintenance?
Big data for predictive maintenance refers to the large volumes of data generated by IoT sensors and other sources. This data is processed and analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that help predict equipment failures. By leveraging big data analytics, organizations can make informed decisions about when and how to perform maintenance, optimizing asset management and operational efficiency.
- How are IoT and AI revolutionizing predictive maintenance?
IoT and AI are revolutionizing predictive maintenance by integrating real-time data collection with advanced analytics and machine learning. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of IoT data to identify patterns and predict equipment failures with high accuracy, enabling more proactive and effective maintenance strategies.
- What criteria can predictive maintenance IoT sensors measure?
Predictive maintenance IoT sensors can measure various parameters including temperature, vibration, humidity, pressure, and fluid levels. These measurements provide insights into the health and performance of equipment, helping to detect anomalies and predict potential failures.
- Why use an IIoT predictive maintenance app for your manufacturing needs?
An IIoT predictive maintenance app offers numerous benefits, including real-time monitoring of equipment, automated data analysis, and timely alerts for maintenance needs. By using such an app, manufacturers can improve maintenance efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize operational performance through data-driven insights.